Publications
Publication Highlights
Growth charts of brain morphometry for preschool children

-
Brain development from 1 to 6 years of age anchors a wide range of functional capabilities and carries early signs of neurodevelopmental disorders. However, quantitative models for depicting brain morphology changes and making individualized inferences are lacking, preventing the identification of early brain atypicality during this period.
- This work reveals age dependence of brain morphometrics in preschool children;
- Constructs growth curve models for cortical thickness and volume of brain regions;
- Proposes typical types of age dependence among cortical and subcortical regions;
- Provides models for individualized evaluation of brain developmental states;
-
Accurate recognition of children with language developmental delay.
- Zhang H, Li J, Su X, Hu Y, Liu T, Ni S, et al. (2022): Growth charts of brain morphometry for preschool children. NeuroImage 255: 119178. full text
Dynamic tracking of state anxiety via multi-modal data and machine learning
- Existing measures of state anxiety, such as the commonly used State Anxiety Inventory (STAI-S), mainly rely on subjective questionnaires with low temporal resolution. Quantitative representations of state anxiety based on psychological and physiological responses are still lacking, which limits the dynamic tracking of changing state anxiety levels in an anxiety-inducing paradigm.
- We propose a state anxiety dynamic tracking model based on psychological and physiological data, which reflects the dynamic changes of individual state anxiety under high temporal resolution.
- This model can accurately measure state anxiety at resting state using only objective and easily accessible physiological signals, providing a sensitive measure of state anxiety level for future research on affective brain-computer interaction and anxiety regulation.
- Ding Y, Liu J, Zhang X, Yang Z (2022): Dynamic Tracking of State Anxiety via Multi-Modal Data and Machine Learning. Front Psychiatry 13: 757961. full text
Impact of inter-individual variability on the estimation of default mode network in temporal concatenation group ICA
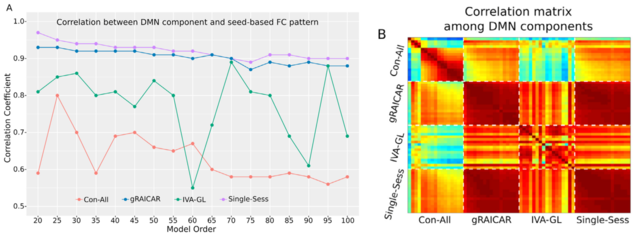
-
We found that inter-subject variability in data impact the performance of temporal-concatenated ICA, a commonly used group-level ICA approach, to estimate the group-level default mode network (DMN).
-
We showed that increased inter-subject variability caused inaccurate estimation of DMN and strong dependence on the number-of-component setting in ICA.
-
This study calls for caution when applying TC-GICA to datasets expected to have large inter-individual variability, such as pooling different experimental groups of subjects
-
Hu Y, Yang Z, 2021. Impact of inter-individual variability on the estimation of default mode network in temporal concatenation group ICA. Neuroimage. full text
Abnormal asymmetry of thalamic volume moderates stress from parents and anxiety symptoms in children and adolescents with social anxiety disorder
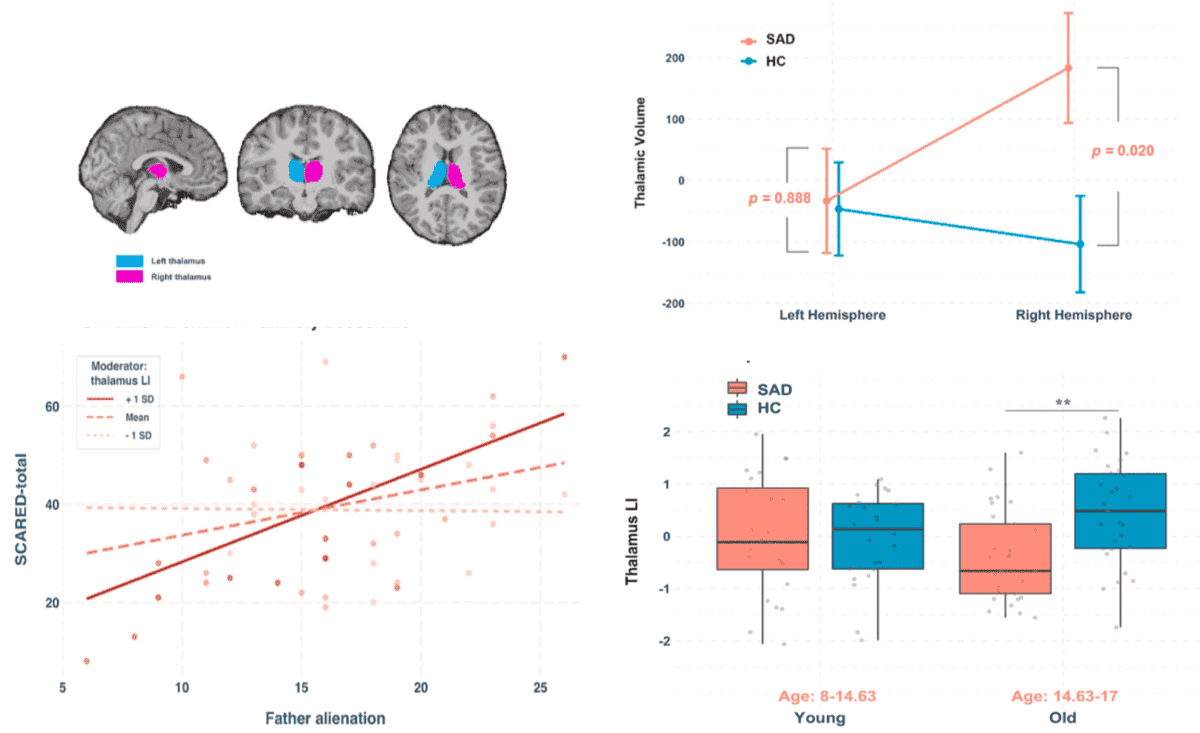
- We found that adolescents with social anxiety disorder exhibit significantly abnormal asymmetry in thalamus volume. This asymmetry becomes more evident in the relative older group (14-17), supporting brain developmental abnormalities in children and adolescents with SAD.
- This asymmetry significantly weakens the relationships between parental attachment and the overall anxiety level of adolescents. The findings further reveal the interactions between physiological and chronic stress in children and adolescents with SAD.
- Zhang Y, Liu W, Lebowitz ER, Zhang F, Hu Y, Liu Z, Yang H, Wu J, Wang Y, Silverman WK, Yang Z, Cheng W, 2020. Abnormal asymmetry of thalamic volume moderates stress from parents and anxiety symptoms in children and adolescents with social anxiety disorder. Neuropharmacology.full text
Reliability maps of individual differences reflected in naturalistic imaging
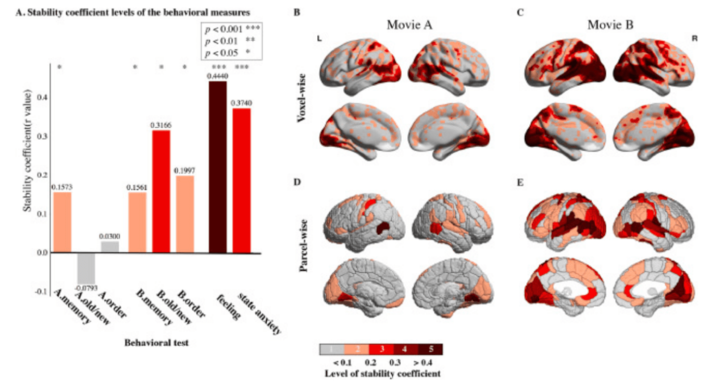
- This paper presents voxel-wise and parcel-wise test-retest reliability maps of individual variability reflected in naturalistic imaging. We found that 1/3 voxels reflected reliable inter-individual similarity in an emotion-evoking movie.
- Some regions exhibited “trait-like” inter-individual similarity and reliability. That is, the inter-individual similarity remained stable between the two movie-viewing sessions with a 1-week interval, and the reliability of the inter-individual similarity remained consistent across different contents of the emotion-evoking movie.
- Gao, J., Chen, G., Wu, J., Wang, Y., Hu, Y., Xu, T., Zuo, X., Yang, Z., 2020. Reliability map of individual differences reflected in inter-subject correlation in naturalistic imaging. Neuroimage 223, 117277. full text
- We share the resultant reliability maps here: https://osf.io/dnkg8/
A naturalistic imaging approach for individualized psychiatric imaging
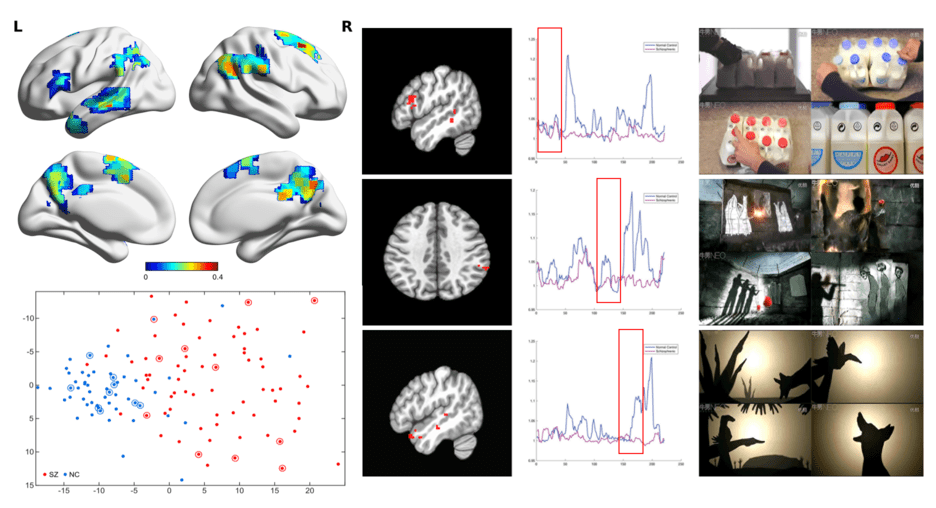
- We developed a naturalistic imaging approach that helps to identify schizophrenia patients when they watch a movie in an MRI scan. This approach does not assume a common brain response of patients and, therefore, it is suitable for psychiatric applications where biological heterogeneity is a significant issue.
- Yang, Z., Wu, J., Xu, L., Deng, Z., Tang, Y., Gao, J., Hu, Y., Zhang, Y., Qin, S., Li, C., Wang, J., 2019. Individualized psychiatric imaging based on inter-subject neural synchronization in movie watching. Neuroimage. full text
Altered gray matter volume and structural co-variance in adolescents with social anxiety disorder
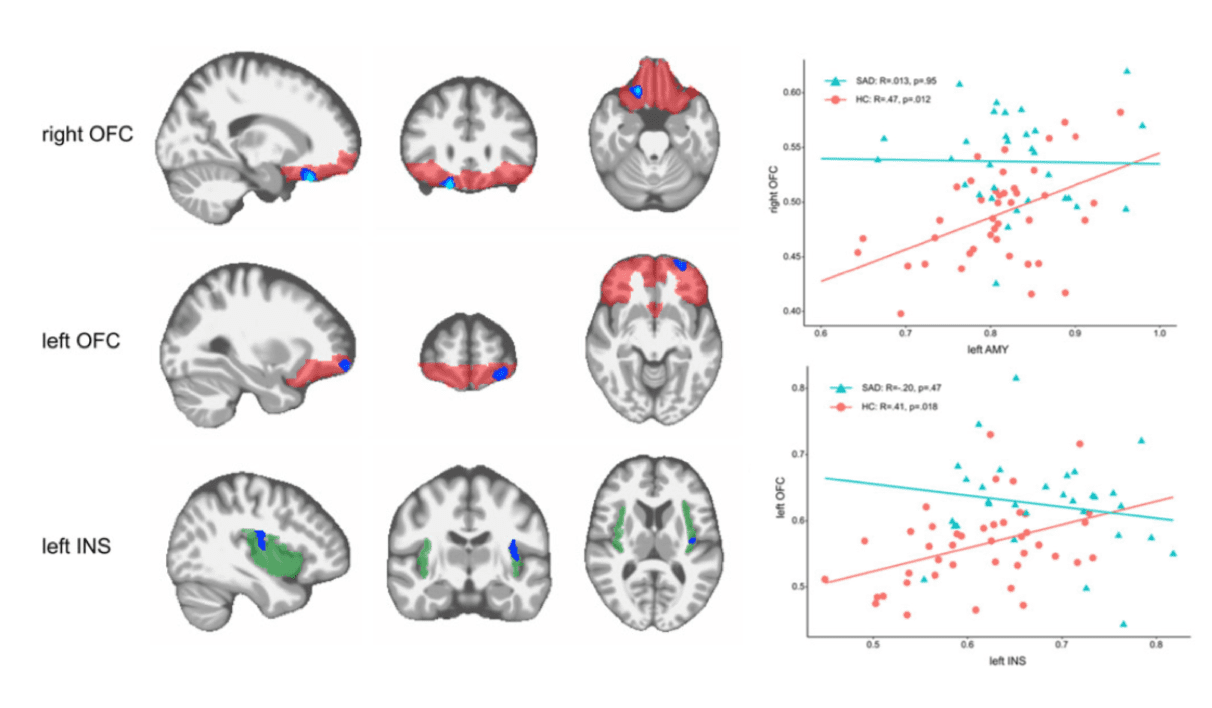
- We provided evidence for a delayed and unsynchronized development of the fronto-limbic system of adolescents with social anxiety disorder. We found significant co-variance in grey matter volume of orbitofrontal gyrus, insula, and amygdala in typically developing adolescents, but this co-variance relationship was disrupted in adolescents with social anxiety disorder.
- Liu, Z., Hu, Y., Zhang, Y., Liu, W., Zhang, L., Wang, Y., Yang, H., Wu, J., Cheng, W., Yang, Z., 2020. Altered gray matter volume and structural co-variance in adolescents with social anxiety disorder: Evidence for a delayed and unsynchronized development of the fronto-limbic system. Psychol. Med. full text
Deficits in precuneus network are associated with auditory hallucinations in Schizophrenia
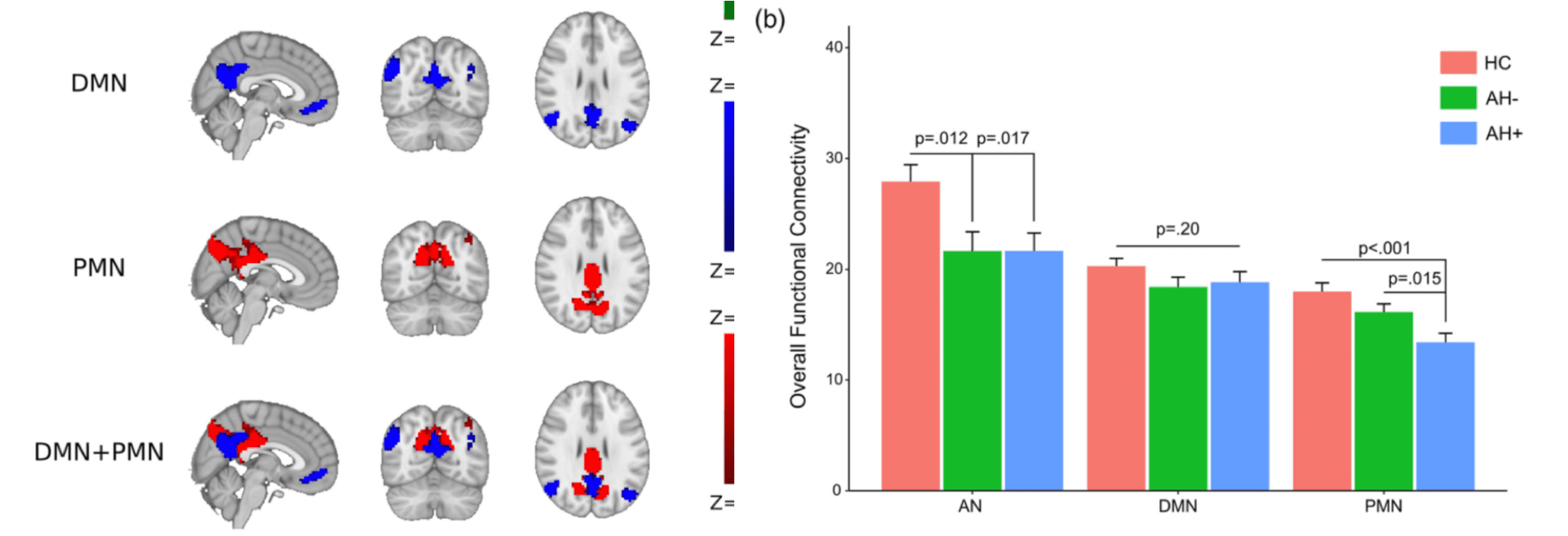
- In a sample of first-episode drug-naive schizophrenia patients and matched healthy controls, we found that the functional connectivity within the precuneus network (PCN) distinguishes the schizophrenia patients with auditory hallucinations from those without auditory hallucinations and the healthy controls. In contrast, we did not detect a significant inter-group difference in the functional connectivity of the default mode network (DMN). These findings support different roles of PCN and DMN in functional connectivity deficits in schizophrenia.
- Guo, Q., Hu, Y., Zeng, B., Tang, Y., Li, G., Zhang, T., Wang, Jinhong, Northoff, G., Li, C., Goff, D., Wang, Jijun, Yang, Z., 2020. Parietal memory network and default mode network in first-episode drug-naïve schizophrenia: Associations with auditory hallucination. Hum. Brain Mapp. full text
Publication list
2022
-
Hu, Y., Li, Q., Qiao, K., Zhang, X., Chen, B., Yang, Z., 2022. PhiPipe: A multi-modal MRI data processing pipeline with test-retest reliability and predicative validity assessments. Human Brain Mapping, Published Online full text
-
Liu, J., Xie, S., Hu, Y., Ding, Y., Zhang, X., Liu, W., Zhang, L., Ma, C., Kang, Y., Jin, S., Xia, Y., Hu, Z., Liu, Z., Cheng, W., Yang, Z., 2022. Age‐dependent alterations in the coordinated development of subcortical regions in adolescents with social anxiety disorder. European Child & Adolescent Psychiatry, Published Online full text
-
Li, W., Cui, H., Li, H., Colcombe, S., Smith, R., Cao, X., Pang, J., Hu, Q., Zhang, L., Yang, Z., Wang, J., Li, C., 2022. Specific and common functional connectivity deficits in drug-free generalized anxiety disorder and panic disorder: A data-driven analysis. Psychiatry Research, 319, 114971. full text
-
Jiang, L., Qiao, K., Li, Q., Hu, Y., Zhang, X., Wang, J., Peng, D., Fan, Q., Zhao, M., Sheng, J., Wang, J., Li, C., Fang, Y., Wang, Z., Yang, Z., for the Psychiatric Imaging Consortium, 2022. Categorical and dimensional deficits in hippocampal subfields among schizophrenia, obsessive-compulsive disorder, bipolar disorder, and major depressive disorder. Biological Psychiatry: Cognitive Neuroscience and Neuroimaging, Published online. full text
-
Zhang, H., Li, J., Su, X., Hu, Y., Liu, T., Ni, S., Li, H., Zuo, X.-N., Fu, J., Yuan, T.-F., Yang, Z., 2022. Growth charts of brain morphometry for preschool children. NeuroImage 255, 119178. full text
-
Ding, Y., Liu, J., Zhang, X., Yang, Z., 2022. Dynamic Tracking of State Anxiety via Multi-Modal Data and Machine Learning. Front. Psychiatry 13, 757961. full text
-
Zhang, Q., Li, B., Jin, S., Liu, W., Liu, J., Xie, S., Zhang, L., Kang, Y., Ding, Y., Zhang, X., Cheng, W., Yang, Z., 2022. Comparing the Effectiveness of Brain Structural Imaging, Resting-state fMRI, and Naturalistic fMRI in Recognizing Social Anxiety Disorder in Children and Adolescents. Psychiatry Research: Neuroimaging 111485. full text
2021
-
Xie, S., Zhang, X., Cheng, W., Yang, Z., 2021. Adolescent anxiety disorders and the developing brain: comparing neuroimaging findings in adolescents and adults. Gen Psych 34, e100411. full text
-
Li, Q., Jiang, L., Qiao, K., Hu, Y., Chen, B., Zhang, X., Ding, Y., Yang, Z., Li, C., 2021. INCloud: integrated neuroimaging cloud for data collection, management, analysis and clinical translations. Gen Psych 34, e100651. full text
-
Hu, Y., Yang, Z., 2021. Impact of inter-individual variability on the estimation of default mode network in temporal concatenation group ICA. Neuroimage 237, 118114. full text
-
Xu, Z., Zhang, Xiaoyun, Chang, H., Kong, Y., Ni, Y., Liu, R., Zhang, Xiaolin, Hu, Y., Yang, Z., Hou, M., Mao, R., Liu, W.-T., Du, Y., Yu, S., Wang, Z., Ji, M., Zhou, Z., 2021. Rescue of maternal immune activation-induced behavioral abnormalities in adult mouse offspring by pathogen-activated maternal Treg cells. Nat Neurosci 24, 818–830. full text
-
Zeng, Y., Tao, F., Cui, Z., Wu, L., Xu, J., Dong, W., Liu, C., Yang, Z., Qin, S., 2021. Dynamic integration and segregation of amygdala subregional functional circuits linking to physiological arousal. NeuroImage 238, 118224. full text
-
Jiang, L., Cui, H., Zhang, C., Cao, X., Gu, N., Zhu, Y., Wang, J., Yang, Z., Li, C., 2021. Repetitive Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation for Improving Cognitive Function in Patients With Mild Cognitive Impairment: A Systematic Review. Frontiers in Aging Neuroscience 12, 593000. full text
2020
- Gao, J., Chen, G., Wu, J., Wang, Y., Hu, Y., Xu, T., Zuo, X., Yang, Z., 2020. Reliability map of individual differences reflected in inter-subject correlation in naturalistic imaging. Neuroimage 223, 117277. full text
- Zhang, Y., Liu, W., Lebowitz, E.R., Zhang, F., Hu, Y., Liu, Z., Yang, H., Wu, J., Wang, Y., Silverman, W.K., Yang, Z., Cheng, W., 2020. Abnormal asymmetry of thalamic volume moderates stress from parents and anxiety symptoms in children and adolescents with social anxiety disorder. Neuropharmacology.full text
- Cheng, W., Zhang, F., Liu, Z., Zhang, H., Lyu, Y., Xu, H., Hua, Y., Gu, J., Yang, Z., Liu, J., 2020. A psychological health support scheme for medical teams in COVID-19 outbreak and its effectiveness. Gen. Psychiatry 33, e100288. full text
- Guo, Q., Hu, Y., Zeng, B., Tang, Y., Li, G., Zhang, T., Wang, Jinhong, Northoff, G., Li, C., Goff, D., Wang, Jijun, Yang, Z., 2020. Parietal memory network and default mode network in first‐episode drug‐naïve schizophrenia: Associations with auditory hallucination. Hum. Brain Mapp. hbm.24923. full text
- Liu, Z., Hu, Y., Zhang, Y., Liu, W., Zhang, L., Wang, Y., Yang, H., Wu, J., Cheng, W., Yang, Z., 2020. Altered gray matter volume and structural co-variance in adolescents with social anxiety disorder: Evidence for a delayed and unsynchronized development of the fronto-limbic system. Psychol. Med. full text
- Cheng, W., Zhang, F., Hua, Y., Yang, Z., Liu, J., 2020. Development of a psychological first-aid model in inpatients with COVID-19 in Wuhan, China. Gen. Psychiatry. full text
- Cui, H., Zhang, B., Li, W., Li, H., Pang, J., Hu, Q., Zhang, L., Tang, Y., Yang, Z., Wang, J., Li, C., Northoff, G., 2020. Insula shows abnormal task-evoked and resting-state activity in first-episode drug-naïve generalized anxiety disorder. Depress. Anxiety 37, 632–644. full text
2019
- Zhang, Y., Xu, L., Hu, Y., Wu, J., Li, C., Wang, J., Yang, Z., 2019. Functional Connectivity Between Sensory-Motor Subnetworks Reflects the Duration of Untreated Psychosis and Predicts Treatment Outcome of First-Episode Drug-Naïve Schizophrenia. Biol. Psychiatry Cogn. Neurosci. Neuroimaging 4, 697–705. full text
- Yang, Z., Wu, J., Xu, L., Deng, Z., Tang, Y., Gao, J., Hu, Y., Zhang, Y., Qin, S., Li, C., Wang, J., 2019. Individualized psychiatric imaging based on inter-subject neural synchronization in movie watching. Neuroimage 216, 116227. full text
- Xu, T., Zhao, Q., Wang, P., Fan, Q., Chen, J., Zhang, H., Yang, Z., Stein, D.J., Wang, Z., 2019. Altered resting-state cerebellar-cerebral functional connectivity in obsessive-compulsive disorder. Psychol. Med. 49, 1156–1165. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0033291718001915
- Jiang, L., Cao, X., Jiang, J., Li, T., Wang, J., Yang, Z., Li, C., 2019. Atrophy of hippocampal subfield CA2/3 in healthy elderly men is related to educational attainment. Neurobiol. Aging 80, 21–28. full text
- Deng, Z., Wu, J., Gao, J., Hu, Y., Zhang, Y., Wang, Y., Dong, H., Yang, Z., Zuo, X., 2019. Segregated precuneus network and default mode network in naturalistic imaging. Brain Struct. Funct. 224, 3133–3144. full text
- Zhao, Q., Xu, T., Wang, Y., Chen, D., Liu, Q., Yang, Z., Wang, Z., 2019. Limbic cortico-striato-thalamo-cortical functional connectivity in drug-naïve patients of obsessive-compulsive disorder. Psychol. Med. 1–13. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0033291719002988
- Hu, Y., Du, W., Zhang, Y., Li, N., Han, Y., Yang, Z., 2019. Loss of Parietal Memory Network Integrity in Alzheimer’s Disease. Front. Aging Neurosci. 11, 1–15. full text
2018
- Wang, J., Hu, Y., Li, H., Ge, L., Li, J., Cheng, L., Yang, Z., Zuo, X., Xu, Y., 2018. Connecting Openness and the Resting-State Brain Network: A Discover-Validate Approach. Front. Neurosci. 12, 1–9. full text
- Sun, L., Xu, H., Zhang, J., Li, W., Nie, J., Qiu, Q., Liu, Y., Fang, Y., Yang, Z., Li, X., Xiao, S., 2018. Alcohol consumption and subclinical findings on cognitive function, biochemical indexes, and cortical anatomy in cognitively normal aging Han Chinese Population. Front. Aging Neurosci. 10, 1–7. full text
2017
- Syed, M.A., Yang, Z., Hu, X.P., Deshpande, G., 2017. Investigating Brain Connectomic Alterations in Autism Using the Reproducibility of Independent Components Derived from Resting State Functional MRI Data. Front. Neurosci. 11, 459. full text
- Liu, S., Wang, L., Lin, S., Yang, Z., Wang, X., 2017. Analysis and prediction of team performance based on interaction networks, in: Chinese Control Conference, CCC. pp. 11250–11255. full text
- Wei, G.-X., Gong, Z.-Q., Yang, Z., Zuo, X.-N., 2017. Mind-Body Practice Changes Fractional Amplitude of Low Frequency Fluctuations in Intrinsic Control Networks. Front. Psychol. 8. full text
- Zhu, Y., Yang, Z., Zhao, J., Li, T., Wang, M., Qian, J., Jiang, Y., Wang, J., Weng, X., Yu, D., Li, C., 2017. Can interpersonal hypersensitivity under subconscious condition explain paranoid symptom in schizophrenia? Asia-Pacific Psychiatry 9, e12221. full text
2016
- Yang, Z., Zuo, X-N., McMahon, K,L., Craddock, R.C., Kelly, C., de Zubicaray, G.I., Hickie, I., Bandettini, P.A., Castellanos, F.X., Milham, M.P., Wright, M.J. (2016). Genetic and environmental contributions to functional connectivity architecture of the human brain. Cerebral Cortex. 26:2341-2352. full text
- Hu, Y., Wang, J., Li, C., Wang, Y.S., Yang, Z., Zuo, X.N., 2016. Segregation between the parietal memory network and the default mode network: effects of spatial smoothing and model order in ICA. Sci. Bull. 61, 1844–1854. full text
- Yang, Z., Qiu, J., Wang, P., Liu, R., Zuo, X.N., 2016. Brain structure–function associations identified in large-scale neuroimaging data. Brain Struct. Funct. 221, 4459–4474. full text
2015
- Wu, J., Zhang, S., Li, W., Qin, S., He, Y., Yang, Z., Buchanan, T.W., Liu, C., Zhang, K., 2015. Cortisol awakening response predicts intrinsic functional connectivity of the medial prefrontal cortex in the afternoon of the same day. Neuroimage 122. full text
- Yang, Z., Zuo, X-N., 2015. Big neuroimaging data-informed mind-brain association studies: Methodology and applications. Chinese Sci. Bull. (Chinese Version) 60, 966. full text
- Chen, B., Xu, T., Zhou, C., Wang, L., Yang, N., Wang, Z., Dong, H.M., Yang, Z., Zang, Y.F., Zuo, X.N., Weng, X.C., 2015. Individual variability and test-retest reliability revealed by ten repeated resting-state brain scans over one month. PLoS One 10, 1–21. full text
- Jiang, L., Hou, X.H., Yang, N., Yang, Z., Zuo, X.N., 2015. Examination of local functional homogeneity in autism. Biomed Res. Int. 2015, 12–14. full text
- Jiang, L., Xu, Y., Zhu, X.-T., Yang, Z., Li, H.-J., Zuo, X.-N., 2015. Local-to-remote cortical connectivity in early- and adulthood-onset schizophrenia. Transl. Psychiatry 5, e566–e566. full text
- Xu, T., Yang, Z., Jiang, L., Xing, X.X., Zuo, X.N., 2015. A Connectome Computation System for discovery science of brain. Sci. Bull. 60, 86–95. full text
2014
- Yang, Z., Chang, C., Xu, T., Jiang, L., Handwerker, D.A., Castellanos, F.X., Milham, M.P., Bandettini, P.A., Zuo, X.N., 2014a. Connectivity trajectory across lifespan differentiates the precuneus from the default network. Neuroimage 89, 45–56. full text
- Yang, Z., Xu, Y., Xu, T., Hoy, C.W., Handwerker, D.A., Chen, G., Northoff, G., Zuo, X.-N.N., Bandettini, P.A., 2014b. Brain network informed subject community detection in early-onset schizophrenia. Sci. Rep. 4. full text
- Yang, Z., Huang, Z., Gonzalez-Castillo, J., Dai, R., Northoff, G., Bandettini, P., 2014. Using fMRI to decode true thoughts independent of intention to conceal. Neuroimage 99, 80–92. full text
- Zuo, X.-N., Anderson, J.S., Bellec, P., Birn, R.M., Biswal, B.B., Blautzik, J., Breitner, J.C.S., Buckner, R.L., Calhoun, V.D., Castellanos, F.X., Chen, A., Chen, B., Chen, J., Chen, X., Colcombe, S.J., Courtney, W., Craddock, R.C., Di Martino, A., Dong, H.-M., Fu, X., Gong, Q., Gorgolewski, K.J., Han, Y., He, Ye, He, Yong, Ho, E., Holmes, A., Hou, X.-H., Huckins, J., Jiang, T., Jiang, Y., Kelley, W., Kelly, C., King, M., LaConte, S.M., Lainhart, J.E., Lei, X., Li, H.-J., Li, Kaiming, Li, Kuncheng, Lin, Q., Liu, D., Liu, J., Liu, X., Liu, Y., Lu, G., Lu, J., Luna, B., Luo, J., Lurie, D., Mao, Y., Margulies, D.S., Mayer, A.R., Meindl, T., Meyerand, M.E., Nan, W., Nielsen, J.A., O’Connor, D., Paulsen, D., Prabhakaran, V., Qi, Z., Qiu, J., Shao, C., Shehzad, Z., Tang, W., Villringer, A., Wang, H., Wang, K., Wei, D., Wei, G.-X., Weng, X.-C., Wu, X., Xu, T., Yang, N., Yang, Z., Zang, Y.-F., Zhang, L., Zhang, Q., Zhang, Zhe, Zhang, Zhiqiang, Zhao, K., Zhen, Z., Zhou, Y., Zhu, X.-T., Milham, M.P., 2014. An open science resource for establishing reliability and reproducibility in functional connectomics. Sci. Data 1, 140049. full text
- Huang, Z., Dai, R., Wu, Xuehai, Yang, Z., Liu, D., Hu, J., Gao, L., Tang, W., Mao, Y., Jin, Y., Wu, Xing, Liu, B., Zhang, Y., Lu, L., Laureys, S., Weng, X., Northoff, G., 2014. The self and its resting state in consciousness: An investigation of the vegetative state. Hum. Brain Mapp. 35, 1997–2008. full text
- Jiang, L., Xu, T., He, Ye, Hou, X.H., Wang, J., Cao, X.Y., Wei, G.X., Yang, Z., He, Yong, Zuo, X.N., 2014. Toward neurobiological characterization of functional homogeneity in the human cortex: regional variation, morphological association and functional covariance network organization. Brain Struct. Funct. 220, 2485–2507. full text
- Tang, L.-R., Liu, C.-H., Jing, B., Ma, X., Li, H.-Y., Zhang, Y., Li, F., Wang, Y.-P., Yang, Z., Wang, C.-Y., 2014. Voxel-based morphometry study of the insular cortex in bipolar depression. Psychiatry Res. Neuroimaging 224, 89–95. full text
- Wei, G.X., Dong, H.M., Yang, Z., Luo, J., Zuo, X.N., 2014. Tai Chi Chuan optimizes the functional organization of the intrinsic human brain architecture in older adults. Front. Aging Neurosci. 6, 1–10. full text
- Yang, Z., Wu, P., Weng, X., Bandettini, P.A., 2014. Cerebellum engages in automation of verb-generation skill. J. Integr. Neurosci. 13, 1–17. full text
2013
- Wang, M., Zhao, J., Qian, J., Zhu, Y., Yang, Z., Jiang, Y., Wang, J., Du, Y., Weng, X., Li, C., 2013. Binocular rivalry in children with schizophrenia: the conscious and unconscious cognitive processing of interpersonal information. Shanghai Arch. Psychiatry 25, 157–164. full text
- Li, S., Lee, K., Zhao, J., Yang, Z., He, S., Weng, X., 2013. Neural competition as a developmental process: Early hemispheric specialization for word processing delays specialization for face processing. Neuropsychologia 51, 950–959. full text
- Liu, C.H., Ma, X., Wu, X., Zhang, Y., Zhou, F.C., Li, F., Tie, C. Le, Dong, J., Wang, Y.J., Yang, Z., Wang, C.Y., 2013. Regional homogeneity of resting-state brain abnormalities in bipolar and unipolar depression. Prog. Neuro-Psychopharmacology Biol. Psychiatry 41, 52–59. full text
- Wei, G.X., Xu, T., Fan, F.M., Dong, H.M., Jiang, L.L., Li, H.J., Yang, Z., Luo, J., Zuo, X.N., 2013. Can Taichi Reshape the Brain? A Brain Morphometry Study. PLoS One 8. full text
- Zuo, X-N., Xu, T., Jiang, L., Yang, Z., Cao, X.Y., He, Y., Zang, Y.F., Castellanos, F.X., Milham, M.P., 2013. Toward reliable characterization of functional homogeneity in the human brain: Preprocessing, scan duration, imaging resolution and computational space. Neuroimage 65, 374–386. full text
2012 and before
- Yang, Z., Zuo, X.N., Wang, P., Li, Z., LaConte, S.M., Bandettini, P.A., Hu, X.P., 2012. Generalized RAICAR: Discover homogeneous subject (sub)groups by reproducibility of their intrinsic connectivity networks. Neuroimage 63, 403–414. full text
- Liu, C.H., Li, F., Li, S.F., Wang, Y.J., Tie, C. Le, Wu, H.Y., Zhou, Z., Zhang, D., Dong, J., Yang, Z., Wang, C.Y., 2012. Abnormal baseline brain activity in bipolar depression: A resting state functional magnetic resonance imaging study. Psychiatry Res. - Neuroimaging 203, 175–179. full text
- Yang, Z., Fang, F., Weng, X., 2012. Recent developments in multivariate pattern analysis for functional MRI. Neurosci. Bull. 28, 399–408. full text
- Xu, G., Jiang, Y., Ma, L., Yang, Z., Weng, X., 2012. Similar spatial patterns of neural coding of category selectivity in FFA and VWFA under different attention conditions. Neuropsychologia 50, 862–868. full text
- Yang, Z., Zhao, J., Jiang, Y., Li, C., Wang, J., Weng, X., Northoff, G., 2011. Altered negative unconscious processing in major depressive disorder: an exploratory neuropsychological study. PLoS One 6, e21881. full text
- Huang, Z., Zhang, J.X., Yang, Z., Dong, G., Wu, J., Chan, a S., Weng, X., 2010. Verbal memory retrieval engages visual cortex in musicians. Neuroscience 168, 179–89. full text
- Yang, Z., LaConte, S., Weng, X., Hu, X., 2008. Ranking and averaging independent component analysis by reproducibility (RAICAR). Hum. Brain Mapp. 29, 711–725. full text








